Java Programming
Friday, January 24th
Interested in a career as a first responder? Check out this event on Saturday, Feb. 8th
Review of primitive types - A primitive is a "built-in" data type - it comes with JAVA.
Review of Type Casting - int X = (int) Y; this is required if Y is of type Long and is NOT an integer.Why are variables always declared at the beginning of the class?
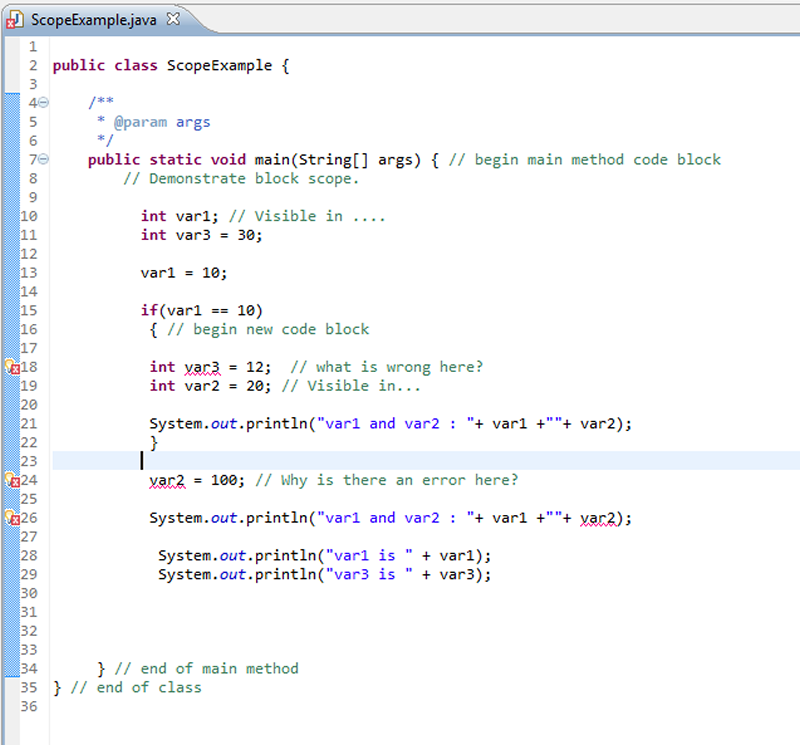
Example of the scope of variables - see below0b0101, 0x56AC, 56.304f
Operator Precedence + - / * % ++ --
How can you override precedence?
Modulus operator %
Pre-increment vs Post-increment
implicit type conversions - smaller into bigger is OK but the reverse is NOT allowed.
Using the Java API (or Google)
Relational Operators
Logical Operators
Complete Section 4 Lesson 3: Data Types and Operators slides
Complete Section 4 Lesson 3: Data Types and Operators practice
Complete Section 4 Lesson 3: Programming with Data Types and Operators practice on school loop
Show me your TriangleArea calculator - prob #1, FieldTrip calculator - prob #3, and the rest of the questions. Do the math calculations - prob #2 only after you have finished problems 1 & 3.
The final output for the Triangle Area should look like this: The area of a triangle with a base of ____ and a height of ___ is _____. Thank you for using the Triangle Area Calculator. This program is brought to you byThe final output for the Field Trip program should look like this:Your field trip with ______people will require ______busses and _____ vans. Thanks for using the field trip calculator. This program was brought to you by
Problem 2:For the MathPractice problem use the following values for the variables for A-C
double x = 3.0;
double y = 5.0;
double z = 4.0;
double answer = 0.0;
For problems D-F make y=2.0 Your output should show the following for each problem:
Problem A.
X = 3.0 - show the actual values of all variables used in the formula, in this case only X
The answer is 3.848701079585163
Homework
Install Eclipse on your home computer if you would like to be able to work on your java at home.
What
In this lesson, you will learn how to:
• Create a WHILE loop
• Create a DO-WHILE loop
• Input characters from the keyboard during program execution
• Use the full form of the IF statements and FOR loops
• Apply switch in Java code
• Use break effectively in Java code
• Rewrite a Java program to prompt the user for input and perform a mathematical calculation
Why
When creating code that needs to execute logic more than once, loops become a very useful tool.
Loops are central to programming and primarily work to change the flow of a program similar to conditional statements like IF and ELSE.
Loops help you simplify your code while allowing you the flexibility to repeat code execution with ease.
How
By completing the slides, quiz and practice exercises.