Java Programming
Thursday, April 9th
Creating the multiplyArray( ) method
Today you will create your multiplyArray(int[][]array1, int[][]array2, int[][] array3) method. Unlike the add and subtract array methods that made use of nested for loops this method requires that you hard code the calculations. Here are the instructions from Oracle:
Multiplication of matrices appears to be confusing since it does not follow the positional method used in addition and subtraction. The answer is achieved by taking the row from the first matrix and the column from the second matrix and multiplying the respective values and then taking the sum of the products.
The answer below was achieve as follows:
3(1)+4(-2)=-5 3(0)+4(3)=12
5(1)+6(-2)=-7 5(0)+6(3)=18The first step for solving this problem is to write down the array and index values for each number shown above. Here are the index values for a two by two array:
[0][0], [0][1]
[1][0], [1][1]
Using these index values the number 3 above comes from array1[0][0]
The 1 comes from array1[0][0]. These two values would be multiplied together and then added to the product of the next two numbers 4 and -2. The final answer is then stored in array3. Setup your first equation and see if the answer matches the -5 that is provided. If it does then your first line works. Now copy the line but change the index values so the correct numbers are pulled from array1 and array2. Repeat this process until you have all four calculations completed.
Use the values shown below to test your code:
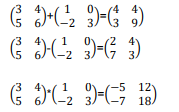
One last method and your Matrix program will be complete.
Write a program that take in two matrices and then allow the user to choose to add, subtract, or multiply them and display the answer. The program will display the following menu:
1. Enter Matrix A - display the Matrix so the output look like the actual matrix, not just a list of numbers.
2. Enter Matrix B - display the Matrix so the output look like the actual matrix, not just a list of numbers.
3. Display A + B - display the output so it is in the form of the actual matrix answer, not just a list of numbers.
4. Display A - B
5. Display A * B
6. Exit
The program should loop and allow the user to continue to choose different options until they choose quit. The well written program will modularize the process into different methods.
Suggested methods:
fillArray(Scanner input, int[][] array)
printArray(int [][] array)
addArray(int[][]array1, int[][]array2, int[][] array3)
subtractArray(int[][]array1, int[][]array2, int[][] array3)
multiplyArray(int[][]array1, int[][]array2, int[][] array3)
How to Crash Proof Your Code - Exception Handling Demonstration
Three Types of Errors
Complete Section 6 Lesson 3: Handling Errors slides
Complete Section 6 Lesson 3: Handling Errors quiz and show your results for teacher check
Complete work on the Section 6 Lesson 3: Handling Errors practice on school loop.Section 6.3 Program Problem:
Create new class called Crash and create an array of five names and then prompt the user for a number of the name they want to see. Loop the program until the user enters 99 to exit the program. Once the program is working crash it by entering a number that is not in the array. Then crash the program again by entering a letter instead of a number. Pay attention to the errors that are produced.Create a new class called CrashProof and copy the code from the Crash class into this new class. Now add a try/catch block to handle the two errors that were used to crash the previous program. You will need two catch blocks since there are two errors. You will also need to import the appropriate error classes. Each error should provide an appropriate message to the user. Include in the fix for the letter a .nextLine(); statement to clear the input buffer of the letter the user entered other wise you will end up in an infinite loop.
Begin Section 7 Lesson 1: Passing Objects and Overloading Methods slides
Complete7 Lesson 1: Passing Objects and Overloading Methods quiz and show your results for teacher check
Complete work on the7 Lesson 1: Passing Objects and Overloading Methods practice on school loop.
Homework
Have a wonderful spring break!
What
In this lesson, you will learn how to:
•Recognize the correct general form of a class
• Create an object of a class
• Describe object references
• Create methods that compile with no errors
• Return a value from a method
• Use parameters in a method
Why
Class templates are the foundation of the Java language. Understanding how to create a class with various methods will be essential to becoming a good Java programmer. Knowing how to instantiate an object and compare it to other objects is critical to learning to use and work with Java data types.
How
By completing the slides, quiz and practice exercises.